Generative AI holds the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our world. Unlike previous AI technologies, it focuses on generating contextual and meaningful content, powered by a combination of machine and deep learning.
For business leaders, incorporating generative AI into their organizations can lead to revenue growth, cost reduction, innovation, and more. However, it’s crucial to apply this technology thoughtfully, understanding its core principles and techniques, and aligning them with specific use cases to maximize benefits while mitigating risks.
We heard someone’s chatbot got a bit creative with their refund policy – and now they have to honor it!
An airline’s chatbot (who has now been fired) provided inaccurate information about the airline’s bereavement travel policy to a passenger. Here’s what happened: on the day Jake’s grandmother died, he visited the company’s website to book a flight from Vancouver to Toronto. Unsure of the airline’s bereavement rates, Jake asked the company’s chatbot to explain. It recommended him to book a flight immediately and then request a refund within 90 days. In reality the airline’s policy does not provide refunds for bereavement travel after the flight is booked. Jake attempted to follow the chatbot’s advice and request a refund but was shocked when his request was rejected!
Check out the full story here.
What we want to say is: yes, GenAI can take off the load (in that case a chatbot) but be careful with its implementation! It can never replace a human interaction 😉

Let’s come back to the original theme of this article, this guide will provide an overview of generative AI fundamentals, typical business applications, strategies for integration, and safeguards against potential pitfalls.
To grasp the potential and limitations of generative AI, one must comprehend the essence of large language models (LLMs), which form the backbone of this technology.
LLMs are AI systems capable of processing vast amounts of data, contextualizing it, personalizing responses, and providing natural language-based solutions. These models excel in understanding and generating human-like text, facilitating more nuanced interactions with users. Generative AI encompasses various approaches, including language models, image generators, and generative adversarial networks (GANs).
Unlike earlier AI models, generative AI operates on a significantly larger dataset and can manage billions of parameters. This immense scale enables it to perform tasks such as writing poetry and generating images from text.

Despite its potential, generative AI is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it requires careful consideration to determine its suitability for specific organizational needs and compliance with data privacy regulations. While building custom LLMs demands substantial investments, businesses can leverage existing models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google’s Bard through open APIs. By integrating these models with proprietary data, organizations can enhance operational efficiency and address unique challenges effectively.
While generative AI has a lot of promise, it’s important to understand that generative AI is not a ready-made solution and is instead a versatile technology.
Generative AI is utilized to automatically generate text, aiding in crafting personalized messages, creating web, social media, or email content, and tailoring written material to specific requirements.

Generative AI finds applications in design, marketing, and gaming by transforming word prompts into images. It assists in training, architectural visualizations, and creating blueprints for distributed systems.

In an age driven by visual experiences, generative AI expedites video production, particularly beneficial for augmented reality (AR) and advertising, reducing the need for extensive manual editing.
Generative AI enables the categorization and analysis of large datasets, facilitating the identification of common themes and trends, thereby supporting informed decision-making and targeted strategies.

Generative AI offers real-time language translation, valuable for customer-facing roles. As more large language models (LLMs) are trained in different languages, translation quality and availability continue to improve.

Generative AI enhances the developer experience by acting as an AI assistant, guiding developers in coding tasks, and offering structured information for effective problem-solving.
According to a Bloomberg Intelligence report, the generative AI market is projected to soar to $1.3 trillion within the next decade, a significant increase from its $40 billion market size in 2022. While this rapid growth may initially raise concerns about job displacement, research indicates that generative AI actually enhances worker productivity.
A recent study conducted by MIT revealed that participants tasked with using ChatGPT for a writing assignment experienced a 37% improvement in writing quality, content quality, and originality compared to assignments without the technology. Additionally, task completion times were reduced by 10 minutes. Similarly, the National Bureau of Economic Research found that generative AI increased productivity among customer support advisors by 14%, as measured by the number of issues resolved per hour.
These findings underscore the strategic benefits of integrating generative AI into business operations. By automating simple and repetitive tasks, generative AI allows workers to focus on more impactful endeavors, thereby enhancing overall productivity and efficiency. It’s essential to recognize that the goal of generative AI implementation isn’t to replace workers but to empower them to deliver higher-quality output.
An ecommerce company is leveraging generative AI to revolutionize its image search and recommendation system, transforming the customer shopping experience. Through this cutting-edge system, the company can swiftly analyze images and provide real-time product recommendations based on visual similarities. By harnessing machine learning capabilities, the company’s AI learns and adapts to individual customer preferences, delivering personalized product suggestions tailored to each customer’s browsing and purchasing history. This approach enhances customer engagement and satisfaction by streamlining the product discovery process and offering relevant recommendations.

A longstanding credit card company is harnessing state-of-the-art generative AI technology to enhance customer support through its mobile app and website. This AI-driven system aids customers in account management, fraud detection and prevention, and optimizing reward programs. Equipped with advanced natural language processing capabilities, the system allows customers to ask questions using their own language and receive personalized responses tailored to their inquiries. This innovative approach improves customer satisfaction and efficiency in resolving issues, ultimately enhancing the overall customer experience.

Incorporating generative AI solutions into your organization may initially appear overwhelming, but breaking down the process into manageable steps can simplify the task. The first crucial step towards embracing generative AI is to establish an experience vision. This involves defining a clear vision of the desired customer experience, which will serve as a guiding principle for designing and delivering your final product or service.
Executive alignment through an experience vision is vital to kickstart your journey with generative AI. Here’s how your organization can benefit from establishing an experience vision for AI adoption:
Once your experience vision is refined and your team is motivated, it’s time to implement your generative AI strategies.
Once you’ve identified appropriate use cases for your organization and outlined your objectives, you can proceed to test them in a proof of concept (POC). This approach involves minimal investment, reduces wasted effort, and enhances outcomes, bringing you closer to innovative solutions.
Before initiating the development of your proof of concept, it’s essential to address specific risks associated with generative AI:
By addressing these risks and developing a proof of concept, you can validate the feasibility and effectiveness of generative AI solutions within your organization, paving the way for successful implementation and innovation.
To initiate a proof of concept for generative AI, it’s crucial to establish clear objectives and success criteria. This facilitates the evaluation of the solution’s effectiveness and its impact on the business. Here’s a step-by-step plan outlining the implementation process, data requirements, and evaluation methods:

By conducting a proof of concept for generative AI, you can explore its potential, enhance customer experiences, and develop innovative solutions to drive business growth. However, before proceeding, it’s essential to address and prepare for the risks associated with generative AI implementation.
Implementing AI on a large scale isn’t as simple as flipping a switch. It’s a complex process that requires careful planning, an ecosystem approach, and governance. However, with the right framework in place, implementing AI and mitigating associated risks is entirely achievable.
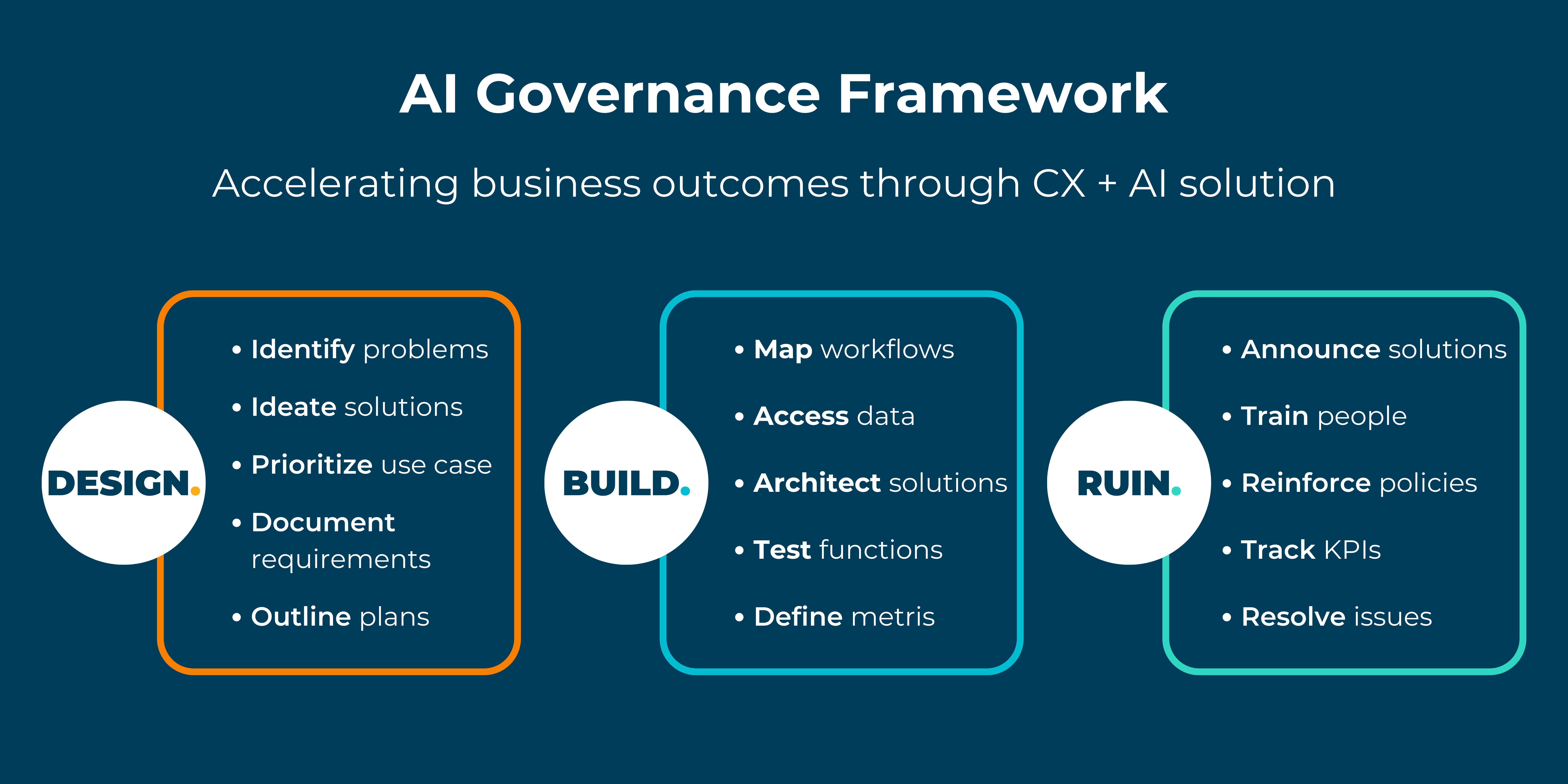
Implementing an AI Governance Framework
Establishing an AI Governance Framework is crucial for navigating this complex terrain successfully. This framework serves as a roadmap for identifying opportunities and risks to both your business and your customers. It all starts with understanding the rules governing AI usage, including legal, compliance, privacy, security, accessibility, and sustainability considerations, all managed through governance.
Given the abundance of conflicting information in the media about AI technology, it’s essential for organizations to communicate the do’s and don’ts of AI, particularly regarding security, privacy, and compliance. For instance, employees must understand that certain AI interfaces, like ChatGPT, are not private, as data processed through them may be reviewed and used for research purposes, potentially breaching confidentiality agreements with customers.
AI governance serves as the cornerstone of this transformative process, ensuring that AI technologies are deployed responsibly and ethically. It involves developing a comprehensive AI governance framework encompassing principles, guidelines, technology controls, and regulations addressing issues such as fairness, accountability, transparency, and privacy. By implementing AI governance, organizations can cultivate a more trustworthy and inclusive customer experience environment, fostering customer loyalty and enhancing brand reputation.
For effective AI governance, it’s imperative to engage multiple internal and external stakeholders, each contributing uniquely to the design, development, and operation of AI initiatives:
To construct a sturdy AI governance framework, organizations should adhere to the following best practices:
Establish principles: A robust AI governance framework should encompass fundamental principles such as ethics, accountability, transparency, and privacy. Develop comprehensive guidelines and policies that address these aspects, ensuring alignment with your organization’s core values and industry standards.
Involve stakeholders: Engage a diverse array of stakeholders in the development and implementation of the AI governance framework. This includes leadership, employees, customers, partners, information security experts, and regulators. By incorporating various perspectives, you can create a more inclusive framework that addresses a broad spectrum of concerns and considerations.
Implement safeguards: Put in place mechanisms to enforce adherence to your AI governance framework. This involves establishing a clear reporting structure that extends to senior leadership, providing comprehensive training on AI ethics for employees, regularly communicating outcomes and findings, conducting routine audits, and delineating clear lines of responsibility for managing AI systems.
Evaluate progress: Given that AI systems evolve over time, it is crucial to continuously monitor their performance and impact. Conduct regular assessments to identify potential biases, privacy issues, or other governance concerns, and take prompt corrective action when necessary to uphold the integrity and effectiveness of the framework.
Foster collaboration: Actively participate in industry forums and foster collaboration with other organizations, academia, and government agencies. By sharing best practices, learning from each other’s experiences, and contributing to the development of AI governance standards, you can establish robust partnerships that facilitate the design, construction, and operation of AI initiatives in the most efficient and cost-effective manner.
While generative AI is a hot topic, only a few companies are taking actionable steps to leverage its potential. Now is the opportune moment to start realizing the value of generative AI.
However, it’s paramount for brands to adopt a human-centric approach, ensuring that generative AI serves its ultimate purpose: enhancing people’s lives. When employed to address real-world challenges, generative AI transcends being just another technology, generating manifold benefits for individuals and businesses alike.
Given generative AI’s transformative capabilities, strategic thinking and adaptation are imperative starting today. To maintain a competitive edge and explore new growth avenues, a comprehensive understanding of generative AI’s underlying technologies, best practices, and limitations is essential. Additionally, businesses must identify suitable use cases and mitigate associated risks effectively.
While this may seem daunting, partnering with experts capable of designing, building, and operating successful generative AI solutions can simplify the process. Leveraging proprietary data, businesses can maximize the advantages offered by generative AI and drive significant benefits across their operations.
GenAI at scale is complex. But don’t worry we provide the enablement you need across the ecosystem to improve CX and reduce costs. Trust us!
